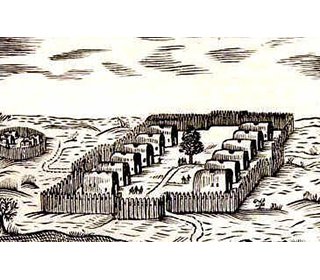
Lenape village of longhouses What clothes did the Lenape wear?
The Lenape clothes were made from animal skins and included long breechclouts, leggings, long cloaks and shoulder to waist length mantles. These were made from the skins of deer (buckskin) raccoon, otter and beaver. Lenape Women wore wraparound skirts, tunics and cloaks. The Europeans introduced trade cloth to the Lenape tribe who then began to change their traditional style of of dress. Lenape Men removed all facial hair and the men and women often colored their faces with red ocre. Tattooing was also common to both sexes, as were nose rings. Older men wore their hair long, but Lenape warriors usually had a scalp lock decorated with a roach headdress that was often dyed a bright red color. The roach headdress was attached to the scalp-lock and stood straight up from the head like a crest. Sometimes feathers were added as additional decorations. What did the Lenape tribe eat?
The food that the Lenape tribe ate included the staple diet of the 'three sisters' crops of corn, beans and squash. Tobacco was also farmed by the men. Fish such as sturgeon, pike and a variety of shellfish such as clams, oysters, lobsters and scallops were an important part of their food supply. The Lenape men also provided meat from deer (venison), black bear and smaller game like squirrel, rabbit, wild turkey and duck. The Lenape food also included nuts, vegetables, mushrooms and fruits (plums, blueberries, strawberries and raspberries). What weapons did the Lenape use?
The weapons used by the Lenape warriors included war clubs, tomahawks, battle hammers, bows and arrows, knives, spears and axes. Lenape History: What happened to the Lenape tribe?
The following Lenape history timeline details facts, dates and famous landmarks of the people. The Lenape timeline explains what happened to the people of their tribe. Lenape History Timeline 8000 BC: Leni Lenape Native Americans occupied New Jersey for thousands of years before European colonization 1609: Henry Hudson was hired by the Dutch East India Company to explore the east coast of North America 1614: The New Netherlands was established 1620: The Great Migration of English colonists and the encroachment of Native Indian lands in New England begins 1634: Epidemics of smallpox and measles are spread by the Europeans 1636: Connecticut was settled by colonists, led by Thomas Hooker 1638: New Sweden colony was established by Peter Minuit along the lower Delaware River from 1638 to 1655. The Lenape in Manhattan sold their lands to Peter Minuit for trade goods worth about 60 guilders (24 dollars) 1639: Willem Kieft arrived in New Netherland to take up his appointment as Governor General of New Netherland 1641: Lenape warriors rebelled against the Dutch when the livestock of colonists destroyed some cornfields of the Raritan Lenape Indians, who lived on Staten Island at the mouth of the Hudson River 1641: Willem Kieft placed a bounty on Raritan scalps, making it profitable for Dutch settlers to kill local Native Indians 1643: Kieft's War (1643–1645) erupted between New Netherland settlers and the native Lenape population in New York 1643: The Pavonia Massacre occurred on February 25, 1643 when Dutch soldiers tortured and murdered Lenape men, women and children. Pavonia was the first European settlement on the west bank of the Hudson River that was part of the province of New Netherland 1643: On October 1, 1643, a force of united Native Indian tribes attacked the homesteads at Pavonia, most of which were burned to the ground. 1647: Peter Stuyvesant is appointed as Willem Kieft's successor 1653: Pavonia became part of the newly formed Commonality of New Amsterdam. Settlers were granted great tracts of Lenape lands 1655: The Dutch conquest of New Sweden 1655: The Peach Tree War. Pavonia was attacked by approximately five hundred Lenape warriors, killing over 100 settlers on September 15, 1655 1659: The Esopus Wars (September 1659 - September 1663) were two localized conflicts between the indigenous Esopus tribe of Lenape Indians and colonialist New Netherlanders in and around Kingston, New York 1664: In September 1664, the Dutch ceded New Netherland to the English 1664: The New Jersey Colony was founded by Lord Berkeley and Sir George Carteret 1682: The Pennsylvania Colony was founded by William Penn 1682: The Leni Lenape, severly diminished in number by warfare and disease, signed treaties of friendship with William Penn, the Quaker founder of Pennsylvania, who established the English colony on the Delaware River. The Quakers spread Christianity amongst the Lenape 1688: The French and Indian Wars (1688-1763) begin marking the outbreak of King William's War (1688-1699) and the western Lenape sided with the French 1702: Queen Anne's War (1702-1713) 1740: Moravian Missions (1740-1837) in Pennsylvania were established by missionaries from Germany 1744: King George's War (1744 - 1748) 1754: French Indian War (1754 - 1763), also known as the 7 year war, was the fourth and final series of conflicts in the French and Indian Wars fought between the British and the French. Both sides were aided by Native Indian allies 1758: The Treaty of Easton between the Lenape and the colonists, required the Lenape to move westward, out of present-day New York and New Jersey and into Pennsylvania, Ohio and Oklahoma 1763: French and Indian War ends in victory for the British ending the colony of New France 1763: The Lenape in Ohio fought the British in Pontiac’s Rebellion (1763 - 1766) A shaman known as Delaware Prophet played an important role in the conflict. 1776: The American War of Independence (1775 - 1783) 1778: The Lenape were the first tribe to sign a treaty with the U.S. government at Fort Pitt in 1778 during the American War of Independence 1785: The Lenape supported the Miami tribe in Little Turtle’s War (1785 - 1795) 1811: The Lenape supported the Shawnee tribe Tecumseh’s Rebellion (1811–1813) 1830: Indian Removal Act 1835 Most of the Lenape tribe in Delaware had been removed to a reservation in Kansas 1845: The population of the Lanape had dropped to less than 2,000 people living in both the United States and Canada. 1867 The Lenape tribe were moved from Kansas to Oklahoma Indian Territory
Lenape History Timeline |